-
Solutions
For personal storage solutions visit these Western Digital brands

BUCKLE UP
Counterpoint Research estimated the storage capacity requirement for autonomous vehicles to balloon over 2TB in the next decade
-
Innovations
ZONED STORAGE
Addresses data center scale with increased capacity, better QoS with lower TCO
Zoned Storage
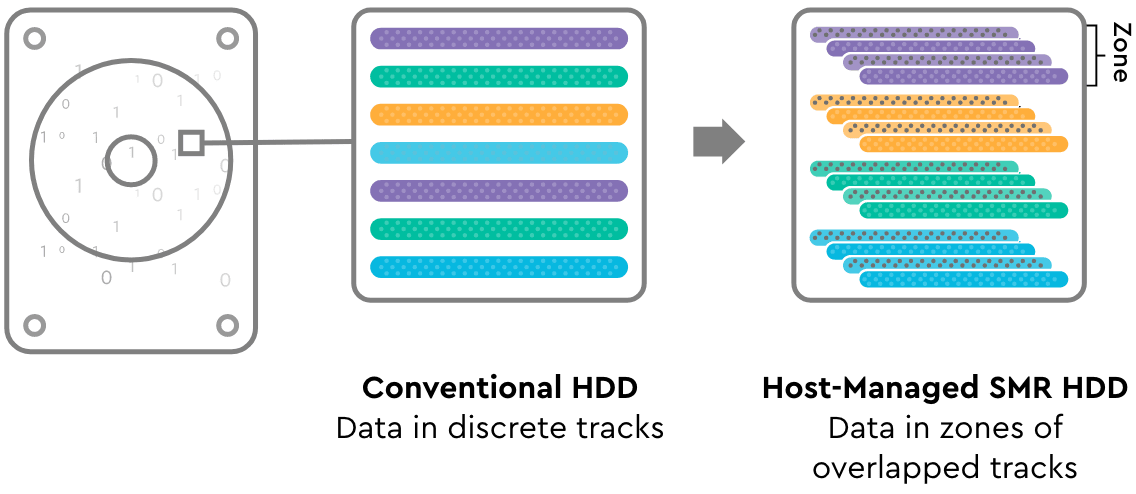
What is SMR?
SMR is an acronym for “Shingled Magnetic Recording,” an important technology utilized to increase capacity and enable lower cost per TB in hard disk drives.
It is primarily used in HDDs that populate the world’s largest cloud data centers. As the amount of data created continues to grow at an ever-increasing pace, cloud service providers are seeking ways to drive down costs to enable new applications and provide the benefits of cloud storage to simplify our lives and increase the value of the services they provide. Connected devices provide the opportunity to capture and share more rich data in the form of photos, video, and audio.
Hard disk drives represent the most cost-effective technology to store data, but the challenge is to continually increase capacity and the amount of data that can be stored on each disk, or “platter” in the drive. Increasing drive capacity and storage density provides multi-dimensional benefits. The cost per TB in the device is reduced along with the cost of the corresponding infrastructure in the data center, including real estate, racks, servers and networking equipment.
So how does SMR contribute to this cost reduction? Every platter in a disk drive stores data in a track format. To increase capacity, those tracks have to be written narrower and narrower, while maintaining some space or buffer between discreet tracks. This buffer has to be managed in the device to maintain data integrity, even though the physical environment may be challenging due to vibration created by the cooling fans in the system. SMR circumvents this challenge by writing the tracks in an “overlapping” fashion, much like the shingles on a roof; hence, the name “shingled magnetic recording.”
SMR significantly increases the capacity that can be stored on every disk, improving what we call “areal density” and lowering costs as described above. In a given generation of HDD technology, this could result in approximately 15% additional capacity with cost reduction at both the device and system level.
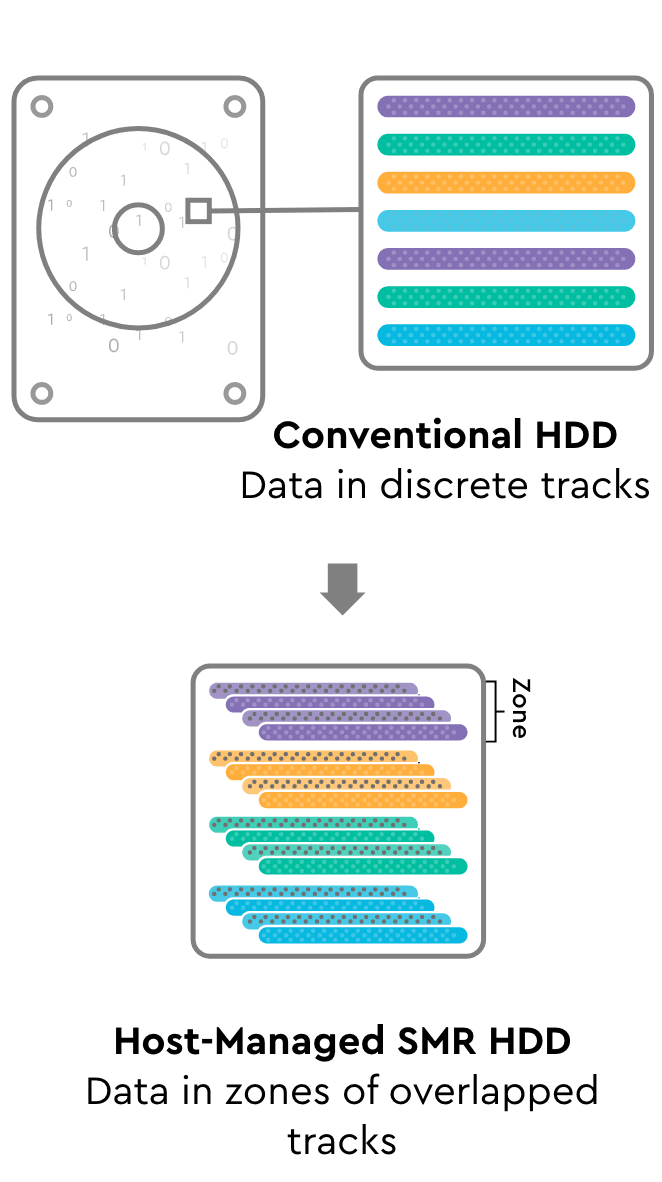
HDDs have historically used CMR, or “conventional magnetic recording,” without shingled tracks nor the requirement to manage sequential zones. CMR drives support completely random read and write operation. Increasingly though, cloud service providers are investing in host software and file systems that can manage the complexities of SMR to deliver cost savings to their customers at scale. This is a trend that is fundamentally re-shaping the cloud data center and will continue to deliver lower cost and higher value data far into the future.
Developers can find development libraries and tools here: https://zonedstorage.io
What is ZNS?
ZNS is an acronym for Zoned Namespaces. It is a NVM Express Consortium standard for zoning SSDs. Back in 2018, the synergies between the raw NAND flash erase block constraints and that of SMR HDDs were readily apparent. In a desire to create a standard for zoning SSDs, similar to SMR HDDs, Western Digital proposed the concept of Zoned Namespaces. ZNS extends the existing SMR HDD zone model to benefit from the mature zone storage stack in Linux and other software ecosystems. By leveraging a common software infrastructure, both ZNS and SMR devices can be incorporated into data center and enterprise systems. All of the data management tasks that are problematic for an SSD controller to handle internally can be addressed if these tasks are instead handled by the host system. The architecture of a ZNS SSD yields the following benefits:

Increased Capacities
Higher density and scale as virtually no over-provisioning is required
Improved Qos
With minimal garbage collection required, the device controller can respond quicker
Reduced Cost
Significantly reduced DRAM requirements and fewer support logic functions are required
Increased Endurance
Because the data is not constantly re-written, the endurance is improved
Challenges for Conventional SSDs
With traditional storage, data is placed on a drive as it arrives. As more-and-more data is written and deleted, data management is required. These necessary actions can tax the drive and negatively impact QoS, limit device density and add cost. For example, in an SSD, data management includes:
Write Amplification
The same host data is rewritten multiple times as the data is moved on the drive
Garbage Collection
Moving, recombining and deleting data to better organize the data
DRAM requirements
Large quantities needed to manage incoming data caching and logical to physical mapping

Over Provisioning
Reserving storage space for internal garbage collection
Data Taken As-Is
Serialize Data
ZNS SSD
The act of implementing Zone Storage on the host allows the system software and hardware to work together more efficiently by eliminating the multiple (duplicated) levels of indirection required for logical to physical mapping between the host and the SSD controller and the file system to the device. ZNS also reduces the need for over-provisioning and removes the issues associated with write amplification and QoS variability. In short ZNS addresses the issues of scale, QoS and TCO which hinder conventional SSDs.
Developers can find libraries and tools at: https://zonedstorage.io